Depending on which side of the argument you take, whether it be technical SEO vs content SEO, you may be missing the point. Content SEO and technical SEO should not be viewed as opposing strategies. Rather, they should be viewed as complementary strategies. When executed alongside one another, they both enhance a website’s visibility on search engines. Technical SEO makes it easy for search engines to access your website, while content SEO tells the search engines how to rank your content.
Think of technical SEO as the construction of the road to your website. Content SEO positions its visitors to take that journey. Without foundational content, compelling content becomes invisible to search engines. Content SEO also makes certain an empty website remains invisible to search engines.
This guide explains how to implement each of these strategies so that you dominate the search engines and the positions they control.

What is Technical SEO?
Technical SEO is the underground layer of your website. It is composed of the backend operations that help search engines discover, crawl, and index your website efficiently. When technical SEO is done poorly, even the best content on your website will be buried deep in the search results.
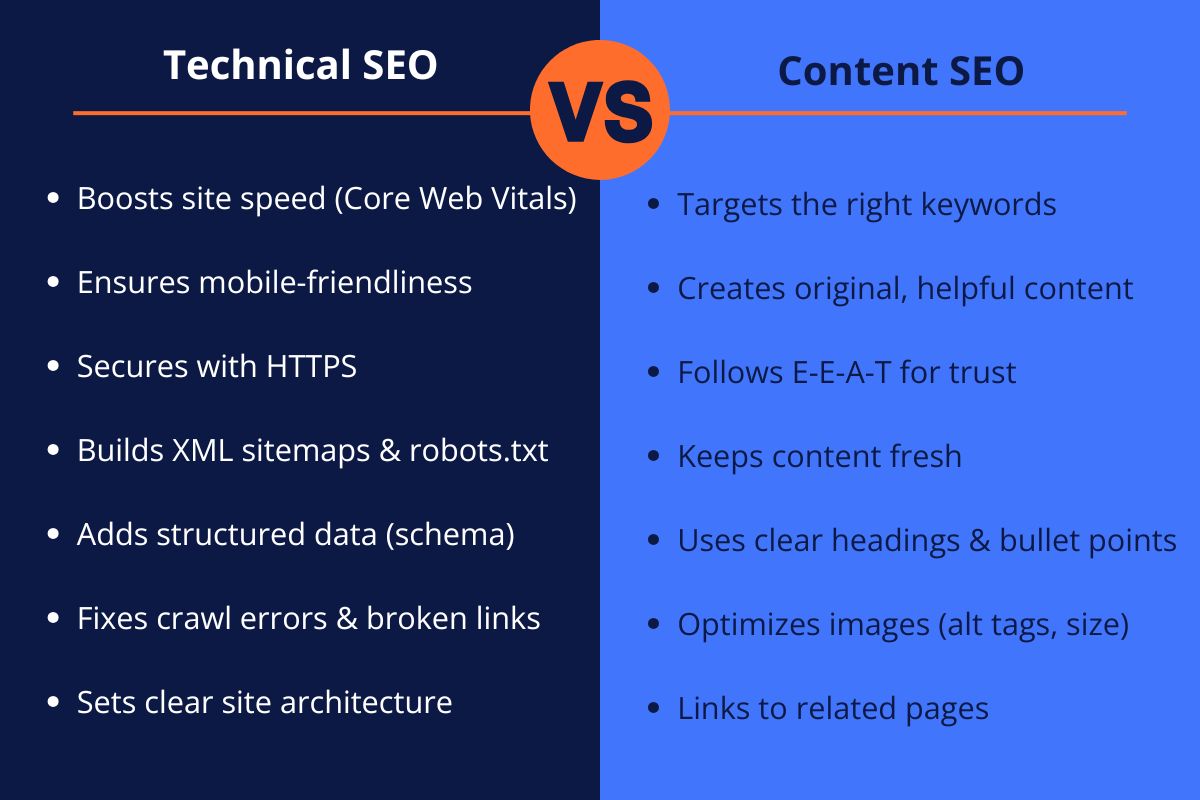
Essential Components of Technical SEO
Core Web Vitals and Site Speed
Google evaluates and ranks websites based on Speed and user experience. It evaluates three important metrics, known as Core Web Vitals.
- Largest Contentful Paint (LCP): measures the time in seconds it takes to load the main content.
- First Input Delay (FID): measures the time in seconds it takes for the user to interact with the element on the page.
- Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS): measures the visual stability of the page as it loads.
If a website scores poorly on any of the above metrics, it could receive a penalty, regardless of the quality of the content.
Mobile-First Optimization
Google has stated that over 60% of searches are conducted on a mobile device. Google uses mobile-first indexing, which means it evaluates the mobile version of the site to make ranking decisions. Because of this, responsive design isn’t a choice; it’s a requirement, and it is important to blend mobile responsive design with Technical SEO and Content SEO.
Crawl Budget and Site Architecture
Each search engine has a limited budget for how much it can crawl on a website. Poor site architecture means that the budget gets wasted on duplicate or low-value pages. This can be improved by:
- Having clear and simple URL structures
- Creating a logical hierarchy within the site
- Using XML sitemaps to direct crawlers to important pages
- Using Robots.txt files to block crawlers from less important pages
- Security and HTTPS
Google uses HTTPS to verify that a website is less likely to be malignant and it has stated that HTTPS is a ranking factor. Websites that do not have an SSL certificate will display warnings stating that they are not secure, and this will greatly decrease the potential for conversion.
Implementation of Markup Data
Rich snippets appear to searchers who use certain words and phrases in their search. Markup data provides better contextual understanding to the search engine, allowing the search engine to more accurately determine if the particular search warrants displaying the rich snippet of info.
Canonicalization and Indexing
Search engines index various segments of a web page. Identifying the web page that you want to be indexed helps to solve the problem. A canonical tag tells Google the page you want to be indexed, and helps to eliminate duplicate content. Indexing helps potential search engine users identify the valuable content they want to index, and helps to remove info that users do NOT want to see.
The invisibility of Technical SEO is what makes the rest of the visibility come to life. Technical SEO is the type of work that makes the rest of the work possible.
What is Content SEO?
The content that online users are able to see is the content that satisfies search user intent and that the search engines trust. Content SEO is about developing, optimizing, and structuring the web content in a way that will respond to and answer the questions that the users are asking.
Fundamental Components of Content SEO
Strategic Keyword Research
Content SEO starts with the audience. What do they want to know? Even when there is high search volume, thoroughly evaluate:
- Search intent (informational, navigational, transactional, commercial)
- Keyword difficulty and competition
- Longer variations of the keywords that indicate specific needs
- Question-based searches to understand the user’s problem
Make sure the target keywords are integrated into the content in a way that makes sense. This ensures that the content will come across as high-quality to both the reader and the search engine.
E-E-A-T
To show E-E-A-T:
- Use Author credentials and bylines
- Use Original research and unique insights.
- Use External citations from reputable sources.
- Use Transparent (clear) information about your business.
- Provide Regular content updates that maintain accuracy.
Content Depth and Comprehensiveness:
Superficial content does not result in a good ranking. Users expect a full and comprehensive answer to their queries.
To achieve that, content:
- Address user intent completely
- Explore subtopics and related questions
- Provide actionable takeaways
- Include supporting data, examples, and visuals
Content Freshness and Updates:
Search engines prioritize content that is frequently updated. Establish a schedule to update content by:
- Changing outdated information and statistics
- Adding new sections covering recent developments
- Updating examples to be relevant
- Improving content depth to align with popular search trends
Internal Linking Strategy
Descriptive Anchor texts and related Internal Links help users find related content. Good internal linking:
- Connects related content with descriptive Anchor texts.
- Creates related pages using Internal Links.
- Directs pages with high authority to pages with high conversion potential.
- Avoid using exact match anchor texts to not over-optimize the internal linking.
Content Organization and Readability
Content should be organized using the following:
- Clean H2 and H3 headers that organize different sections.
- Use subheadings and divide content into Short paragraphs ( 3 sentences or less)
- Use lists that are bulleted.
- Include images and alt text for those images.
- Tables for data comparison
Content SEO drives relevance signals. It is how to build relevance for Google around topical authority and user satisfaction metrics.
Key Differences Between Technical SEO and Content SEO
While both approaches bring the same goal — higher rankings, they operate through different mechanisms:
- Technical SEO ensures search engines can discover, crawl, and index your site. It focuses on architecture and performance.
- Content SEO ensures that what search engines find provides value, relevance, and engagement for users.
Technical SEO answers “Can search engines access this?” Content SEO answers “Should search engines rank this?”
A lightning-fast, perfectly structured site with thin content won’t rank. Brilliant content on a broken, slow site won’t either. Success requires both.
How Do Technical SEO and Content SEO Work Together?
You have content SEO and technical SEO working together to create the best possible outcome.
They each stand alone but work better together.
Here is an example of the best possible outcome:
Scenario 1- The Hidden Masterpiece:
You have a 5,000-word guide that deeply analyzes an industry 5,000 word guide that has it all, with original research, data expert interviews, and even actionable content all put together.
But your site has:
- 8-second load times on mobile.
- No proper XML sitemap submission.
- Has javascript issues that hide content from your site from crawlers.
Even outstanding content is never ranked and lost forever in this content black hole of the internet. This is largely due to the barriers put up by the site. Google relies on positive user experience metrics to make content available, and since the content is not the site is virtually lost.
Scenario 2- The Empty Foundation:
Your site is a technical masterpiece.
- Sub-2 second load times
- Perfect mobile responsiveness
- Flawless structure data
- Efficient use of crawl budget
But I can go on and tell you about your 300-word pages that are about as in-depth as a puddle. They are about as boring as a 300-word page can get, offering nothing of value about a topic that is available everywhere.
Even for a technical masterpiece, the content is as bland as it can get.
Scenario 3: The Winning Combination
You create comprehensive content while making sure that:
- All pages are quick to load
- Search engines can crawl and index everything
- Result displays are enhanced with structured data
- Internal links hierarchically distribute
- Authority mobile users are optimized to experience
Result: The technical aspects hold content visibility while the quality content justifies the ranking. Because of this, the user engagement metrics are kept strong, with sustained engagement reinforcing the ranking over a period.
The balance between content SEO and technical SEO isn’t either/or; it’s both/and. Each amplifies the other’s impact.
Common Mistakes to Avoid with Technical and Content SEO
SEO is an art and a science. It’s easy to slip up. Here are some mistakes that are easy to avoid, regardless of your SEO knowledge.
- Ignoring Core Web Vitals: Creating content is a huge part of your online presence, but without a proper loading speed and other Core Web Vitals, Google will not rank you highly. If it takes too long to load, people will leave and not read your content.
- Overlooking mobile users: If your website isn’t optimized for mobile, you are losing a massive source of traffic. Everything from the size of your text, to the responsiveness of your buttons, to horizontal scrolling can affect your ranking.
- Keyword stuffing: People hate reading spam. So do Google and Bing. If you try to rank using the spammy technique known as keyword stuffing, you will be penalized in ranking. Use keywords naturally as you improve the text for readers.
- Neglecting content updates: Failing to update content signals your site’s lack of authority. Schedule quarterly reviews to refresh and update your content’s stats, examples, and recommendations.
- Forgetting internal links: If you don’t have internal links on your page, search engines don’t know to index it, and you leave the page with little SEO value. Pretty much every page needs links to at least one other page.

FAQ
Neither is more critical. Both are vital if you want to rank well. Technical SEO sets up the ground rules for visibility while Content SEO lays the groundwork for high rankings.
If your site is having some serious tech issues (speed, indexing, mobile), fix those first. Without these, even the best content will stay hidden. If your tech SEO is good, but your content is poor, then your focus should be on content.
Do tech audits and update your content at the same time. Plan to fix broken links, slow pages, mobile responsiveness, and indexation. Keep your content calendar full so you’re publishing and updating content frequently and you’ll hit high quality.
Combined tools like Google Search Console to assess technical and content performance together. When traffic declines, assess if the decline is due to technical problems or the quality of content.
The answer is no. Content SEO is one part of On-page SEO. On-page SEO refers to all of the optimization done on the pages themselves. On-page SEO contains:
Quality and optimization of content (Content SEO)
Meta description and title tags
Structure of header tags
Internal linking
Optimization of images
Structure of URLs
Content SEO is about all the material that users interact with, while On-page SEO is about the technical aspects and content.
The results of Technical SEO are seen faster than the results of Content SEO because of instant changes. Improvements like mobile optimization and changes in indexing usually take about 2-4 weeks to see results. On the other hand, Content SEO provides gradual increases in results. Comprehensive Content SEO pieces can sometimes take 3-6 months to reach the highest search engine rankings.
The most successful strategies require continuous work on both aspects, rather than one-off changes of Technical and Content SEO.
Yes, this model seems to work well for business owners. The in-house content team generally does not possess Technical SEO knowledge related to site structure, coding, performance, and optimization. In-house content is usually a better fit for the industry, audience, and brand voice knowledge.
Hybrid models, where specialists handle the technical foundations and strategy, while the in-house team creates the content and uses guidance from outside sources, are also worth considering.
Building Your Integrated SEO Strategy
The best results in technical SEO vs content SEO come from treating them as unified strategy components, not competing priorities.
Start with a technical foundation audit:
- site speed and Core Web Vitals
- mobile responsiveness
- Search Console indexation coverage
- crawl and broken link errors
- structured data
- HTTPS compliance
Then, build your content strategy:
- business-aligned keyword research
- content gap analysis vs competitors
- user intent resources
- fresh content publishing schedules
- high-value content update schedules
- strategic internal topic linking
All technical content and content metrics must be monitored over time. As sites develop, technical issues will likely arise. Content performance will most likely show topic resonance and content gaps.
Businesses that lead search results never have to choose between content SEO vs technical SEO: they are great at both.
Want to Create a Fully Developed SEO Strategy?
The blend of a perfect technical framework with content mastery is a sign of excellence in both areas. IZ SEO consulting offers multi-layered strategies where technical improvements are paired with content enhancement.
Stop viewing technical SEO vs content SEO as separate processes. Integrated strategies provided lasting search visibility and consistent traffic growth.



