Learning SEO terms can be one of the hardest things to face. Because, to be honest, it is almost like learning a foreign language to try to describe the same thing over and over again. However, the second you’ve learned the basic terms, it all starts to fall into place. Whether you are a newbie or you have already been working in this field for years, this guide will help you learn the essential set of SEO terms you will need.
Introduction: What does SEO stand for?
When we bump into the term SEO, we are simply referring to the process of optimizing a website to be more attractive to search engines like Google, or how it is sometimes colloquially referred to as the process of cleaning one’s showroom to make it more visible to a wider audience. The End game? The main goal is to get more organic traffic so people can find your website without you having to run a paid advertisement to get there. Because as long as people are searching for a website that is similar to what you have to offer, you should be at the top of the list of search engines they are using, be it Google’s standard search engine or Google’s Answer GPT. SEO is like a garden; you have to take care of it.
You’re constantly updating the content, modifying the keywords, and ensuring everything is working properly. There are three key types of SEO work:
- On-Page SEO: Everything you do directly on the pages of your website: content, titles, images, and so on.
- Off-Page SEO: Activities outside your website that improve your site’s reputation; for example, other sites linking to you.
- Technical SEO: The behind-the-scenes work to ensure that search engines can read and understand your site.
In addition, we’ll use these two additional categories:
- Local SEO: Focusing on businesses that wish to appear when consumers search for services “near me.”
- Advanced Terminology: The jargon for when you want to go down a rabbit hole.

On-Page SEO: Making Your Web Pages Shine
On-page SEO is when you have to get your hands dirty and do work on the website directly. It is optimizing each page to be as useful and as easy to find as possible for users and search engines alike.
Key Components of On-Page SEO
Keyword Research and Optimization
The best way to describe Keyword Research is as detective work. You are attempting to discover which words and phrases your prospective customers use when they search for your products or services on Google.
It’s not about the guessing game; what you want is to get into the searcher’s head and understand their intention and the competitive space. Keyword Optimization is when you take the golden keywords and attempt to distribute them throughout the content. The problem here is that the content has to feel more organic, people hate reading content that has been generated by AI. The main keywords can be inserted in the following areas:
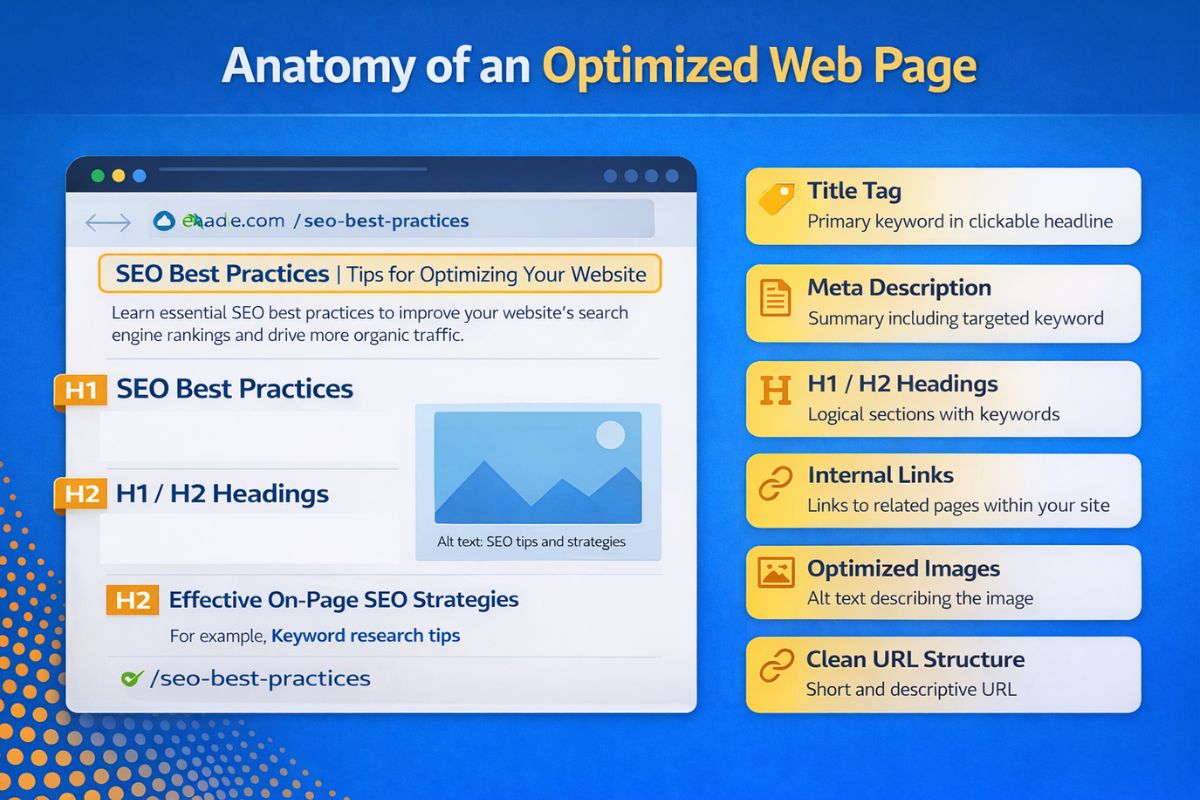
- Title Tag, which is the main clickable headline that people see in search results.
- Meta Description, which is the snippet that shows up below a search result and encourages users to open the link.
- Headers (H1, H2): Headers break the content into sections and make it more readable for the user and the bots that crawl the content
Search Intent Understanding
Understanding search intent boils down to the reason for the user’s search. Are they looking for information? Do they want to purchase something? Do they want to go to a specific website, or are they trying to compare something? Over the years, Google has become very good at matching search results to the search intent. That is why it is important for the content to align with what the user is actually looking for. There are four types of search intent
- Informational: The user is looking for more knowledge or an answer to a specific question
- Navigational: The user is trying to get to a specific website or page
- Commercial: The user is looking into something before they make a purchase
- Transactional: The user is ready to make a purchase or take a specific action
High-Quality Content
When we discuss high-quality content, we do not only mean content that is well written and grammatically perfect (everybody loves that). We mean content that answers users’ questions and is engaging and trustworthy. The content needs to:
- Serve the purpose of the user’s search by solving the problem
- Be readable
- Do not have keyword stuffing. Keywords can and should be used, but in a natural way
- Show real, no-kidding experience and expertise.
It’s not about search engines first, and users second. In fact, the way Google’s Helpful Content System works, if you write content primarily for search engines, your content is not going to rank. Content created primarily for search engines is not going to be ranked. It’s not going to be considered helpful.
AI-Generated Content Considerations
AI Generated Content is everywhere, and Google has made their position abundantly clear. They do not care who created the content. Be it a human or be it an AI on the other side of the code. They only care about helpful, quality content that shows E-E-A-T. When using AI to write content, be sure to:
- Include real human experience and perspective
- Make sure everything is fact-checked to have no mistakes
- Impart personalization and unique insights to the content
- Avoid using templated content and outputs
Meta Tags Optimization
Meta Tags tell search engines about your website. The most relevant ones are title and description since they are the first pieces of information about your page that people read when they see your page on search result when they are looking for info about something. The description and meta tags should contain the main keyword to summarize and describe the content of the page, while being intriguing so that people are tempted to click on the link to the page.
URL Structure
A positive URL Structure is one that is neat and one that details what the page is about. From the following examples, one is more positive than the other.
- www.example.com/seo-terminology-guide (this is a good URL)
- www.example.com/page123?id=xyz (this is a bad URL)
The first URL is good.
Internal and External Linking
Internal links help visitors navigate to related pages of your website by connecting different pages and help search engines understand the website’s structure. External links improve your content by linking to authoritative sites and by adding more credibility to your content. Optimizing External links (linking to other websites) makes it look like you have more evidence to support your content, even if you have none.
Optimized Heading Tag
In a document, heading tags like H1, H2, and H3 are like the different chapters of a book. H1 is usually the title of that section, and the subheadings are H2 and H3.
Image Optimization
image optimization implies that your images should improve the SEO of your site, including descriptive filenames and alt text optimally improve image descriptions. Alt texts, which describe the image, also help blind users understand the image. Alt texts help search engines understand the image.
Content Formatting and User Experience
White space, bullet points, and bold text help improve formatting and enhance the readability of text. If users seem to enjoy the User Experience (UX) of your site, search engines improve your ranking, and vice versa. If users keep bouncing back to the SERP, search engines will lower your ranking.
Important On-Page SEO Terms
- Latent Semantic Indexing (LSI) keywords are terms related to your keyword. If your keyword is, for example, “coffee,” the LSI keywords may be “espresso,” “brewing,” or “caffeine.” LSI keywords help search engines better understand your content.
- Topic Clusters refer to a strategy where a complete pillar page is developed for a broad topic and linked to several related sub-pages, which cover narrower topics. This helps search engines better understand the authoritative breadth and depth of your content.
- Keyword Cannibalization occurs when two or more pages on your domain compete for the same keyword. It’s like people having their own team members fighting each other; nobody wins.
- Content Audit. Your website content gets reviewed systematically to evaluate how each piece is performing to decide what needs to be changed, updated, or deleted. Think of it like a spring cleaning for your website.
- Bounce Rate is proportion of visitors to a website who navigate away from the site after viewing only one page. If the bounce rate is high, this means visitors think the content is irrelevant to what they were looking for.
- Dwell Time is the amount of time a visitor spends on a page before going back to the search results. If users have a long dwell time, this is usually a good sign that the content is aligned with what users were looking for.
Off-Page SEO: Building Your Site’s Perception Online
There is a big difference between perfecting your site with on-page SEO vs off-page SEO, where you work on your brand perception on different platforms. It is like your digital site reputation is getting a word-of-mouth referral.
Off-Page SEO Components
Link Building
Link building is getting other sites to create a hyperlink that directs to your site. Think of a link from a site as a vote for your site’s credibility. Search engines interpret the amount of quality links to your site as an authority.
There are good links, and there are spam links. Here is a breakdown of the quality of different types of links you can get.
- Natural links: the ideal link to get. A site links to your site because they are a loyal customer who appreciates your content.
- Manually Built Links.: Links that you deliberately get through site reputation acquisition.
- Self-Created Links: Links you create on your own, like on the signatures of discussion forums. If done in moderation, you can get some authority from these links, but if done excessively, you can put your site in danger.
Guest Posting
Guest blogging is writing a piece of content for other people’s websites for the purpose of getting exposure for your site, and usually getting a backlink to your site. When done right, you get a win-win. You get to offer content to their readers while you get to increase your reputation and authority.
Social Media Marketing
Social Media Marketing itself will not increase your ranking in a search engine, but it does help your content be seen more easily. When your content is seen, liked, and discussed, it can potentially get more attention from other websites in discussing or linking to the content.
Brand Mentions and Citations
Your business will also gain more presence and authority, by other online platforms simply mentioning your business, or giving it a citation. Even if the citation does not include a link, it will provide a point of reference for a search engine to potentially connect the reference to your business.
Influencer Marketing
While the search engine optimization (SEO) advantages of this could be considered minimal, this style of marketing does provide a great opportunity for business awareness, social sharing, and helpful linking, also known as backlinking. This is especially true when marketing to an audience in your business focus who is already established as an audience leader and has influence.
Forum Posting and Q&A Engagement
Dedicating time to Forum Posting and Q&A Engagement can bring valuable targeted traffic to your site. It is important to provide real content, and not just a bunch of links, if you are hoping to share valuable info.
Content Syndication
When you want to expand your reach, you can republish your original content pieces on different websites through content syndication partnerships. With content syndication, you should check for duplicate content. The re-publisher should include a canonical reference to your original content to avoid duplicate content.
Important Off-Page SEO Terminology
- Backlink: a link from one website to another that form the foundation of off-page SEO.
- Anchor Text: The words in a hyperlink that a user can click. Descriptive anchor text helps explain the linked page to a search engine, which helps in positioning the page with search engines.
- Link Profile: the total accumulation of a website’s backlinks. A good link profile will contain different backlinks from a variety of good-quality websites.
- Link Juice: the authority a site passes to others through backlinks. The more credible the site, the more link juice it will share.
- Trust Flow: a metric that indicates how good and trustworthy a site linking to you is. Better trust flow means more trustworthy links.
- Link Farm: A group of websites that have been made to link to one another and nothing else. This is a big no-no.
- Domain Authority (DA): A score that estimates how well your website will rank in search engines. A higher score indicates a website will rank better and has a higher potential for good SEO.
- Page Authority (PA) – Almost like Domain Authority, but focuses on the ranking power of specific pages of a site instead of the whole site.
- Entity Authority – This is the established trustworthiness of a site on different topics or entities. Google is getting better at understanding a site not just as a bunch of keywords but rather as an entity with defined areas of expertise.
Technical SEO – The Foundation of Everything Else
Technical SEO is the type of SEO that focuses on the behind-the-scenes optimizations that help search engines access, crawl, and understand a site. There is no glitz and glam, but it is an essential part of SEO. Think of it as the plumbing in a house. When the plumbing works, nobody notices it, but when it doesn’t, it is a disaster.
Important Features of Technical SEO
Site Speed
Site speed is the time it takes the pages of a site to load. In a world where people want immediate results, a few-second delay can make a visitor leave the site. Google takes site speed seriously as it is one of the ranking factors and an important part of user experience.
Mobile-Friendliness
More than half the time are conducted via mobile devices. Therefore, your Web platform should function and look great on mobile devices. If a customer has to zoom in and out to read your Web content, you’ve lost the customer.
Mobile-First Indexing
Mobile-First Indexing means that Google rankings are determined by the mobile version of your website. If your mobile version is poorly optimized or lacking content, your rankings are going to suffer, even for desktop searches. Since 2019, this has been the standard, and it is not a prediction; it is a reality.
XML Sitemap
Search engines can be thought of like a customer service, or service, representative that can be given a roadmap of your Web platform; this is what an XML Sitemap is. It will contain your roadmap that has all important pages, and it will allow search engines to crawl and index your content easily.
Robots.txt
The search engine bots are like the students in a classroom, and the teacher is the Web content. The teacher has content that can be crawled, and content that should be ignored. The content that should be ignored is the content that you want to be kept secret, like content that is duplicated or that you want to be kept private.
Canonical URL
Duplicate content can be an issue for SEO, and so are multiple URLs for duplicate content. The use of canonical tags informs search engines of which URL should be prioritized. This helps identify which should be the canonical URL for duplicate content.
Structured Data and Schema Markup
Schema markup and structured data are two ways that can be used to enhance the comprehension of search engines and content. The correct and thoughtful use of these two elements can create enhanced search results, sometimes referred to as rich snippets. An example of this may include enhanced search results that have star ratings, prices, or other added information.
Crawlability and Indexability
Indexability and Crawlability are two sides of the same coin. Each is important when considering SEO. Crawlability is when the search engine bots can access and move around your site. Conversely, Indexability is when the bots can access a page that may be stored and is able to be displayed in the search results. Each of these components is necessary for SEO success.
HTTPS Security
HTTPS is the presence of a small lock icon in your browser, and as a visitor to a website, that makes the connection a bit safer. There is also a potential ranking benefit when using HTTPS. The browsers may indicate that a site is “not secure” when HTTPS is not in place.
Site Architecture
Good website architecture can help the site be easy to navigate for users as well as for search engines. Good website architecture can be a set of clear categories and an optimal site structure, and logical internal linking.
The Optimization of 404 Error Pages
A 404 Error Page pops up when a user tries to access a webpage that is unable to be found. Instead of leaving your visitors to be lost forever, a good 404 page tells your visitors that they hit a dead-end but gives them options to navigate to something useful on your website.
Core Web Vitals
Core Web Vitals are the metrics Google has established for assessing user experience on your website.
- Largest Contentful Paint (LCP) measures how fast the main content of the webpage loads. A good score is anything that is loaded in 2.5 seconds or less.
- Interaction to Next Paint (INP) measures how quickly the page reacts after a user has taken an action on the page. This is the new replacement for First Input Delay as of March 2024, and a good score for this is anything less than 200 ms.
- Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS) measures how much of the content on the web page jumps around as it loads. A good score is anything less than 0.1.
All of these metrics are new ranking factors that are dependent on the user experience on your website.

Technical SEO Terms to Know
- Crawl Budget: The number of pages on your site that will be crawled by search engines over a certain time period. Big websites have to be more careful with their site crawl budget.
- Canonicalization: The process that uses canonical tags to show which version of a web page you want to be displayed to search engines to resolve duplicate content issues.
- Lazy Loading: A strategy that improves initial page load time by postponing the loading of images or other elements until the users scroll down to that part of the page.
- Server-Side Rendering: A technique where the pages are constructed on the server before being sent to the browser. This can be useful to improve SEO and performance for more complex websites.
- Breadcrumb Navigation: The “Home > Category > Product” links that are used to show users their current location on your site and create more internal linking.
- Log File Analysis: The process of looking at server logs to see how search engine bots are crawling your site. This helps identify any problems or inefficiencies with the site crawl budget.
- JavaScript SEO: The process of ensuring that content that is rendered by a JavaScript framework is crawlable and indexable by search engines.
Get More Local SEO Success in Your Area
Local SEO means making your business visible when customers search for your services in their area. If your business has a physical location or serves specific locations, Local SEO is an excellent way to attract nearby customers.
Most Important Elements of Local SEO
Optimizing Your Google Business Profile (GBP)
Your Google Business Profile (formerly Google My Business) is like having a free advertisement on Google. It contains your business information and can be accessed through Google Maps and other Google search results. Users can see business hours, contact information, photos, and customer reviews.
GBP had further advancements, like saying business descriptions created by AI, improved Q&A tools, and more noticeable sections for customer reviews. Keeping your profile updated and managed is the foundation of Local SEO.
Local Citations
Local citations refer to the mentions of your business name, address, phone number, and website (NAPW) on the internet. Local citations show the credibility of your business and help pinpoint the location of your business. The most notable element in Local Citations is the consistency. Your business information should be the same everywhere it appears.
NAPW Consistency
NAPW (Name, Address, Phone, Website) consistency is important, but it seems tedious. If Google sees “123 Main St.” on one website but “123 Main St. Street” on another, it gets confused and thinks it is a different business.
Local Pack
The Local Pack is the three business listings at the top of the search results, along with a map and key business details. Snagging a spot in the Local Pack can add significantly to your visibility and the number of calls you receive.
Geotargeting
Geotargeting refers to the practice of personalizing your marketing or content to a specific location. This could mean creating different location-based pages on your website or running city-specific ads.
Local Keyword Optimization
When a business optimizes Local Keywords, they add location-based modifiers to their keywords, such as “Chicago dentist” or “best pizza downtown Austin.” These keywords are much more likely to match the search queries of those who are looking for services in a particular location.
Reviews and Reputation Management
Reviews on Google, Yelp, and other sites do two things for you: they boost your local SEO, and they help potential customers decide to go to your business. Managing your reputation tends to the reviews, responding to them, and asking happy customers to leave reviews.
Let’s focus on honest customer feedback instead of reviews because Google continues to improve how it identifies fake reviews.
Local Business Schema Markup
Local Business Schema Markup is structured data that gives search engines information like your business hours, address, and services. With this data, you can increase your chances of showing up in rich results or the local pack.
More Advanced SEO Terms
Let’s move on to more advanced concepts. These will help you understand how search engines operate and how to prepare for the algorithm updates.
Advanced SEO Components
Let’s put it all together.
E-E-A-T
When it comes to SEO, the E-E-A-T framework (Experience, Expertise, Authoritativeness, and Trustworthiness) is how Google judges your content. This is especially important for content that relates to people’s health, money, or safety. This is how to build E-E-A-T:
E: Experience – demonstrate first-hand, practical experience with the topic
E: Expertise – show knowledge and skill in your field
A: Authoritativeness – build authority with quality backlinks, mentions, and recognition
T: Trustworthiness – honest and accurate content with proper citations and transparency
Google values experience, first-hand knowledge, and practical knowledge sharing even more than before, hence the addition of “Experience.”
YMYL (Your Money Your Life)
YMYL pages cover content that impacts people’s lives in a big way, whether that be health, finances, law, safety advice, etc. Because these topics are so impactful, Google has much more stringent quality requirements, requiring much stronger quality E-E-A-T metrics to be able to rank well.
Helpful Content System
Helpful Content System is seamlessly integrated with Google’s core algorithm. It rewards content that is created to be helpful, instead of content created just to gain a rank on a search engine. Such signals may be:
- Content that shows having been there first-hand
- Transparency with the users on the main goal of the content
- Content that readers have learned something from
- Experts in the ratio of content being created to the content being reviewed
Entity SEO and Knowledge Graphs
Entity SEO is the optimization of content for search engines in relation to real-world entities, people, places, and things. The Knowledge Graph from Google provides the relations among the entities and their interconnections.
In order to optimize for this kind of SEO, one:
- Does consistent naming throughout one’s digital footprint
- Uses schema markup for data that is organized in a particular way
- Displays a clear topical authority throughout one’s niche
- Acquires mentions in authoritative publications that reference the entity
AI Overviews (formerly Search Generative Experience)
AI Overviews are the Google AI-generated snippets that show at the top of results for a number of search queries. It has changed the search engines tremendously through the direct answer to the question being asked that is provided from numerous sources.
To optimize for AI Overviews:
- Build a detailed writing with unquestionable accuracy
- Use clarity and brevity so that AI can easily read
- Utilize correct schema markup
- Concentrate on being a referenced source instead of obtaining the click
Zero-Click Searches
Zero-Click Searches happen when user queries are answered on the search results without the need to visit any page. This includes featured snippets, knowledge panels, and AI Overviews. The following opportunities provide beneficial brand awareness despite potential traffic challenges:
- Building brand awareness by being a cited source
- The following questions lead to further searches by optimizing content
- Developing content that stimulates further content exploration
Voice Search Optimization
Starting now, prepare your content for the growing number of people using Siri, Alexa, Google, and other voice assistants. This involves:
- Developing a more conversational style
- Concentrating on questions
- Focusing on long-tail keywords
- Providing simple, straightforward answers
- Optimizing for local searches because a lot of voice searches are local
Video SEO
Video SEO means optimizing video content for search engines. This means:
- Using detailed video titles that include keywords
- Including detailed video transcripts or closed captions.
- Using compelling clickable thumbnails
- Adding video schema markup
- Copying video SEO content on searches (YouTube, your own site, etc.)
Rich Snippets & SERP Features
Rich Snippets and SERP Features are types of enhanced search results that contain more information, like star ratings, prices, and FAQs. Beyond the standard blue links, SERP Features include:
- Featured snippets
- Image carousels
- Knowledge panels
- People also ask boxes
- Local packs
- Video results
- Shopping results
- AI views
To optimize for these features, your content will generally need certain schema markup and structuring.
Content Pruning
Content Pruning is the process of cutting content that is either outdated, bad, or has performed poorly, while also making updates. This process is sometimes the right path to take. Removing certain pages that are ‘weak’ can improve the quality of your website to the point where the overall performance can be boosted.
Topic Authority and Topic Clusters
Building Topic Authority is positioning your website as an expert on certain topics. It is earned through:
- Writing detailed ‘pillar’ pages on your key topics, and
- Writing on the correlated ‘sub topics’ of those key topics
- Cross-linking those pieces of content as needed
- Publishing content frequently in that niche
- Earning backlinks and mentions from higher authority pages
This is particularly useful as search engines are now evaluating websites on the authority of a ‘topic’ as a whole rather than optimizing pages on individual keywords.
Passage Ranking
Passage Ranking is the ability of Google to rank certain passages of a website instead of just one page as a whole.

Your SEO Journey: Final Thoughts
As my favorite professor would say, “Don’t be overwhelmed. Everyone started at a smaller point, and no one expects you to know everything right off the bat.” So, take a breath! Focus on one area at a time, and the knowledge will come, one bit at a time.
Even though the industry can be overwhelming, the basics remain the same. Establish your user’s needs, and then build your content strategy to help meet them. Make the content you are providing valuable, establish the technical fundamentals, and procure meaningful and long-lasting interactions to build your site’s trust.
As you move through the stages of learning SEO, keep this guide close. Plastering these principles to your site will help you internalize the process and learn how to think about SEO and how to improve your business.
Good SEO helps users find and interact with your business. Help your users, and everything else will fall into place.
If navigating these evolving SEO complexities feels daunting, working with a trusted partner can make all the difference. Indexed Zone SEO has helped countless businesses cut through the noise and build sustainable organic growth strategies that actually deliver results. Whether you’re just starting out or looking to refine your existing approach, having experienced guidance can accelerate your success and help you avoid costly mistakes.



